Learn about DCOI Requirements in this New White Paper
Prepare your data center for the Data Center Optimization Initiative that took effect in 2016 for federal agencies in the US

Abstract:
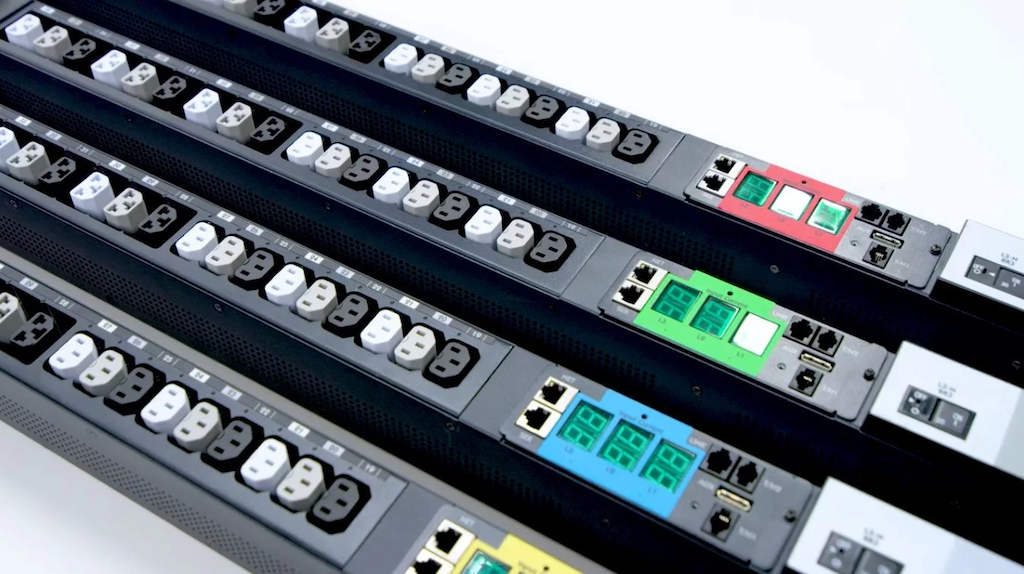
It details the evolution from FDCCI to FITARA to DCOI, with an emphasis on the roles that power measurement and management play in complying with the DCOI requirements for efficiency (through the PUE metric) and reporting through the implementation of a DCIM tool for asset tracking and power monitoring. Details are provided on how the rack and the PDU technology within the rack provide the underlying infrastructure for the base level power monitoring and control that are integral requirements of the DCOI, along with enabling the capacity planning function that leads to intelligent choices for rack and data center consolidation.